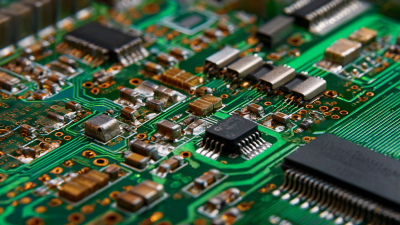
The Future of Electronics: How Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are Revolutionizing Device Design
The rapid evolution of technology has ushered in a new era of device design, where the need for versatility and compactness is more critical than ever. At the forefront of this transformation are flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), which are revolutionizing the way electronic devices are conceived and implemented. Unlike traditional rigid circuit boards, FPCBs offer the remarkable ability to bend, twist, and fold without compromising functionality, thereby enabling manufacturers to create sleek and innovative products. As we delve into the future of electronics, it becomes evident that the integration of FPCBs into various applications not only enhances product performance but also paves the way for groundbreaking advancements in design flexibility and form factor. This significant shift is set to redefine industry standards and consumer expectations, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of electronic devices.

The Evolution of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards: A Technological Milestone
The evolution of flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) marks a significant technological milestone in the electronics industry. As devices become increasingly compact and multifunctional, FPCBs are at the forefront, enabling innovative designs that were previously unimaginable. Their lightweight and adaptable nature allows manufacturers to create devices that can bend and flex, as exemplified by the advancements in foldable smartphones. Major companies continue to refine this technology, enhancing user experience while pushing the boundaries of device capabilities.
In recent news, the commissioning of advanced PCB manufacturing facilities underscores the commitment towards elevating FPCB technologies. The integration of newer innovations, such as the flexible RISC-V microprocessor, showcases a shift towards cost-effective, bendable solutions that promise to redefine electronics. This combination of technological progress and manufacturing advancements is paving the way for smarter, more versatile electronic devices.
Tip: When designing devices with FPCBs, consider the end-user experience to ensure functionality and usability are prioritized. Flexibility should not come at the cost of reliability, so thorough testing in various conditions is crucial. Additionally, staying informed about emerging technologies can provide a competitive edge in product development.
Key Advantages of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards in Modern Electronics
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs) are at the forefront of modern electronics, offering distinct advantages that transform device design. One of the most significant benefits is their lightweight and space-saving design. Unlike traditional rigid boards, FPCBs can bend and fit into compact spaces, allowing for sleeker and more innovative products. This flexibility not only enhances portability but also enables manufacturers to experiment with unique shapes and configurations, paving the way for new opportunities in device aesthetics and functionality.
Tips for integrating FPCBs in your design include starting with a clear understanding of the flexibility required for your application. Consider the environmental factors—which might include temperature or moisture—that your device will face, as these can affect the performance of the circuit. Additionally, engaging with experienced PCB designers early in the process can streamline development, ensuring that both electrical and mechanical needs are met effectively.
Another advantage of FPCBs is their durability. They are less prone to breakage, which is crucial for devices subjected to daily wear and tear. With the ability to withstand high flexing cycles, FPCBs contribute to a longer lifespan for electronic products, reducing replacement costs for consumers and manufacturers alike. This durability does not compromise performance, as FPCBs maintain excellent connectivity and signal integrity, essential for today’s high-speed applications.
Impact of Flexible Circuits on Miniaturization and Device Portability
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) are at the forefront of transforming device design, particularly in the realm of miniaturization and portability. These circuits offer the ability to bend, twist, and fold, allowing for a significantly more compact design without compromising performance. The integration of flexible circuits into consumer electronics facilitates the creation of slimmer devices that can fit into tighter spaces while improving functionality. As a result, manufacturers are no longer constrained by rigid board designs, enabling innovative shapes and user experiences that were previously unattainable.
When incorporating FPCBs, it’s essential to consider the type of micro batteries used to power these devices. Lightweight and efficient power sources, such as thin-film and printed batteries, complement the flexibility and compactness of FPCBs. This combination enhances the overall device usability, particularly in applications such as wearables and IoT devices.
Tips: Ensure that the battery choice aligns with the device’s size and power requirements. Testing various configurations can also help achieve the best balance between performance and space efficiency. Additionally, embracing advances in materials can lead to better thermal management and longer battery life, further enhancing device portability without sacrificing quality.
Applications of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards in Emerging Technologies
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) are at the forefront of innovation in various emerging technologies, enabling new designs and functionalities across multiple sectors. One prominent application of FPCBs can be found in wearable devices, where their lightweight and bendable nature allows for seamless integration with fabric and skin. This adaptability not only enhances comfort but also enables the incorporation of advanced sensors, paving the way for health-monitoring applications that can track biometrics in real-time, offering users personalized health insights.
In the realm of robotics and IoT (Internet of Things), FPCBs facilitate compact device architectures that are essential for miniaturization. Their flexibility allows for more complex interconnections within tight spaces, making it possible to create sophisticated devices that operate efficiently in diverse environments. By expanding the capability of electronic devices to function in varied shapes and confines, FPCBs empower the development of smart appliances and autonomous systems that can be easily deployed in homes and industries, ultimately driving a new wave of technological advancement.
Future Trends: Innovations Shaping the Next Generation of Flexible Electronics
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCs) are at the forefront of innovation in electronic device design, significantly impacting the market landscape. The global FPC market is projected to witness substantial growth, with an estimated value of $33.747 billion, expected to reach approximately $98.25 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.28%. This rapid expansion is driven by advancements in materials and technology, enabling the production of more versatile and compact devices.
Analyzing the FPC market dynamics reveals notable trends in various applications, from automotive to medical. Notably, rigid-flex circuits and multilayer circuits are gaining traction, driven by the increasing complexity of electronic systems and the demand for lightweight designs. Furthermore, the design preferences are evolving with a significant shift towards double-sided and single-sided circuits due to their cost-effectiveness and flexibility in applications spanning consumer electronics, aerospace, and defense sectors. The future promises to be vibrant as innovations in flexible electronics continue to reshape industry standards and consumer expectations.